Building a Simple Second Brain AI Agent with Vercel AI SDK & Maxim AI

A comprehensive step-by-step tutorial on creating a RAG-powered knowledge base system with observability.
Table of Contents
- Project Overview
- Architecture & Technology Stack
- Environment Setup
- Database Configuration
- Embedding System Implementation
- RAG Implementation
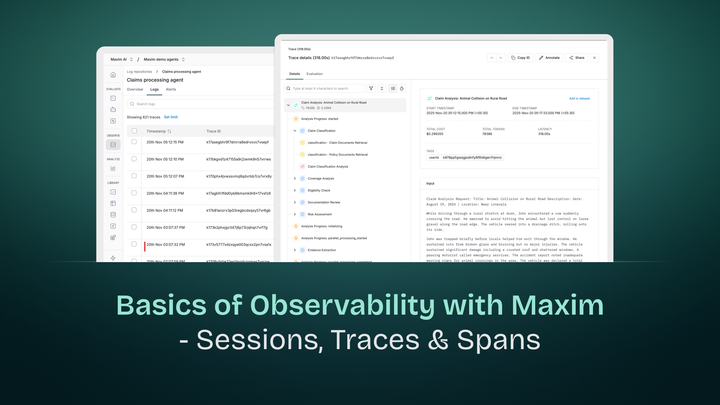
- Maxim AI Integration for Observability
- AI Chat API with Tools
- Frontend Implementation
- Testing & Deployment
- Advanced Features
Project Overview
This tutorial will guide you through building a Second Brain AI Agent - a RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) application that can:
- 🧠 Store and retrieve knowledge using vector embeddings
- 💬 Chat intelligently with context-aware responses
- 🔧 Use tools to save and search information
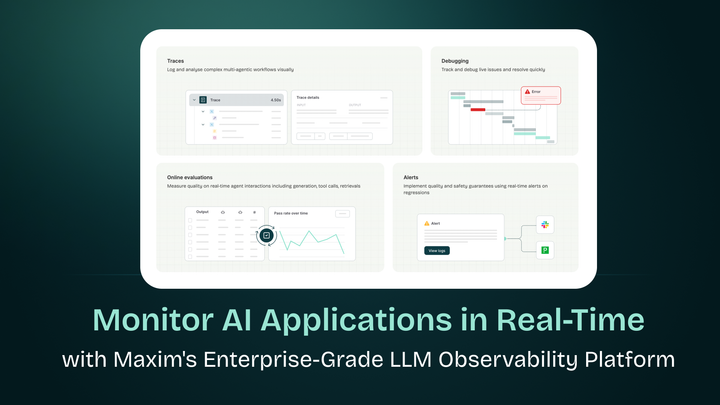
- 📊 Monitor performance with Maxim AI observability
- ⚡ Scale efficiently with PostgreSQL and pgvector
What You'll Build
By the end of this tutorial, you'll have a fully functional AI agent that:
- Accepts user input and intelligently decides when to search its knowledge base
- Automatically saves important information shared by users
- Provides detailed observability insights through Maxim AI
- Offers a beautiful, responsive chat interface
Architecture & Technology Stack
Core Technologies
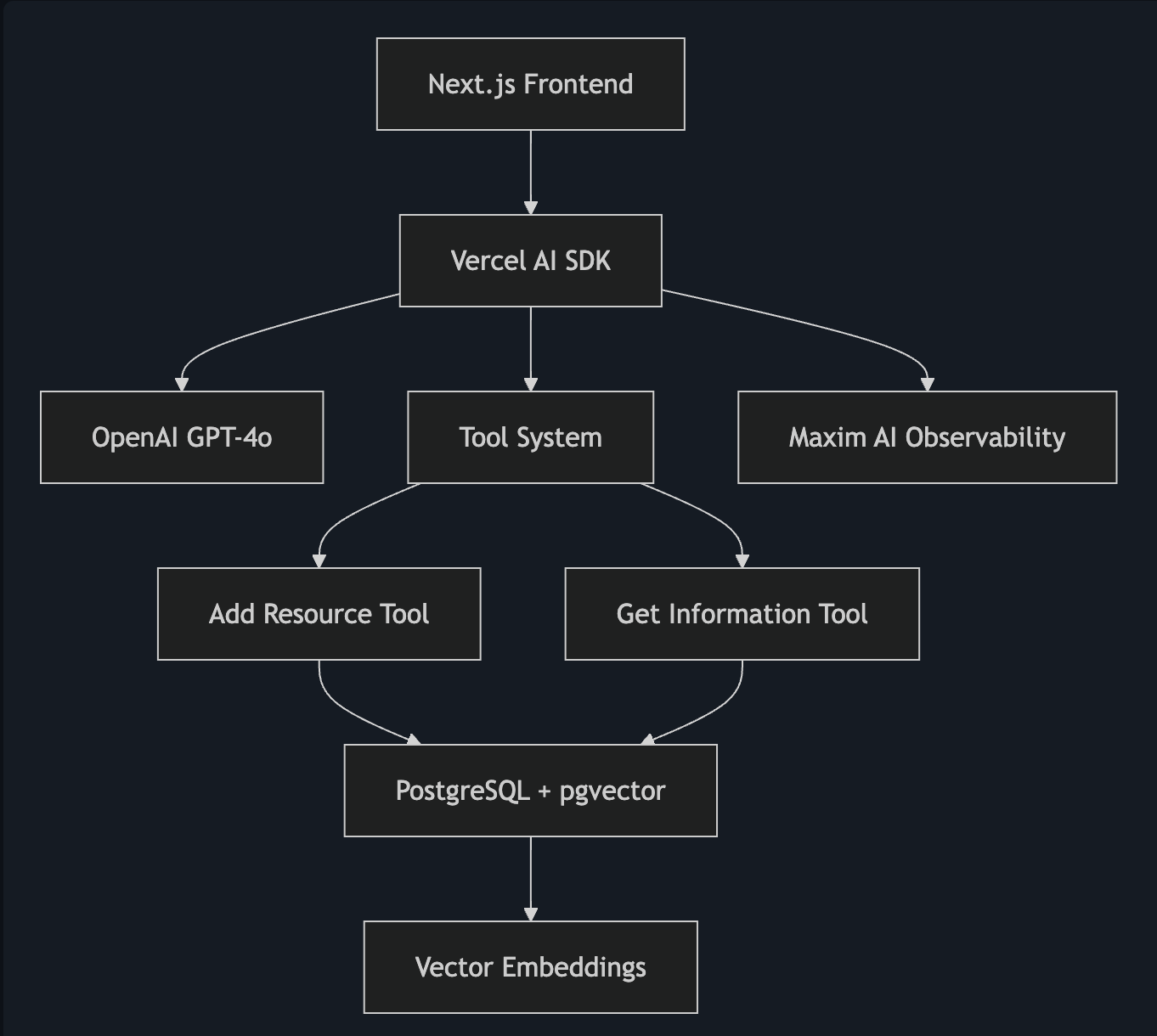
Frontend & Framework:
- Next.js 14 with App Router for the web application
- React 18 with hooks for state management
- TailwindCSS for modern, responsive styling
- shadcn/ui for beautiful UI components
AI & Language Models:
- Vercel AI SDK for streamlined AI integration
- OpenAI GPT-4o for chat completions
- OpenAI text-embedding-3-small for vector embeddings
Database & Storage:
- PostgreSQL as the primary database
- pgvector extension for vector similarity search
- Drizzle ORM for type-safe database operations
Observability & Monitoring:
- Maxim AI for comprehensive AI observability
- Session tracking and performance monitoring
- Detailed logging of tool executions
- Agent Simulation (to be covered in next part)
Watch the walkthrough of this project here -
Environment Setup
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- Node.js 18+ installed
- PostgreSQL with pgvector extension
- OpenAI API key
- Maxim AI account and API key
1. Initialize the Project
# Create a new Next.js project
npx create-next-app@latest ai-second-brain --typescript --tailwind --eslint --app
cd ai-second-brain
# Install required dependencies
npm install @ai-sdk/openai @ai-sdk/react ai drizzle-orm drizzle-zod @maximai/maxim-js
npm install postgres pg @t3-oss/env-nextjs zod nanoid uuid @types/uuid
npm install @radix-ui/react-slot @radix-ui/react-label class-variance-authority
npm install clsx tailwind-merge lucide-react sonner next-themes
# Install development dependencies
npm install -D drizzle-kit tsx @types/pg dotenv
2. Environment Configuration
Create a .env.local file in your project root:
# OpenAI Configuration
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_api_key_here
# Database Configuration
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://username:password@localhost:5432/second_brain_db
# Maxim AI Configuration
MAXIM_API_KEY=your_maxim_api_key_here
MAXIM_LOG_REPO_ID=your_maxim_log_repo_id_here
# Application Environment
NODE_ENV=development
3. Environment Validation
Create lib/env.mjs for type-safe environment variables:
import { createEnv } from "@t3-oss/env-nextjs";
import { z } from "zod";
export const env = createEnv({
server: {
DATABASE_URL: z.string().url(),
OPENAI_API_KEY: z.string().min(1),
MAXIM_API_KEY: z.string().min(1).optional(),
MAXIM_LOG_REPO_ID: z.string().min(1).optional(),
NODE_ENV: z.enum(["development", "test", "production"]).default("development"),
},
client: {},
runtimeEnv: {
DATABASE_URL: process.env.DATABASE_URL,
OPENAI_API_KEY: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
MAXIM_API_KEY: process.env.MAXIM_API_KEY,
MAXIM_LOG_REPO_ID: process.env.MAXIM_LOG_REPO_ID,
NODE_ENV: process.env.NODE_ENV,
},
});
Database Configuration
1. PostgreSQL Setup with pgvector
First, ensure pgvector is installed in your PostgreSQL instance:
-- Connect to your PostgreSQL database and run:
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector;
2. Drizzle Configuration
Create drizzle.config.ts:
import { defineConfig } from "drizzle-kit";
import { env } from "@/lib/env.mjs";
export default defineConfig({
schema: "./lib/db/schema/*",
out: "./lib/db/migrations",
dialect: "postgresql",
dbCredentials: {
url: env.DATABASE_URL,
},
});
3. Database Schema Definition
Create the resources schema in lib/db/schema/resources.ts:
import { sql } from "drizzle-orm";
import { text, varchar, timestamp, pgTable } from "drizzle-orm/pg-core";
import { createSelectSchema } from "drizzle-zod";
import { z } from "zod";
import { nanoid } from "@/lib/utils";
export const resources = pgTable("resources", {
id: varchar("id", { length: 191 })
.primaryKey()
.$defaultFn(() => nanoid()),
content: text("content").notNull(),
createdAt: timestamp("created_at")
.notNull()
.default(sql`now()`),
updatedAt: timestamp("updated_at")
.notNull()
.default(sql`now()`),
});
// Schema for API validation
export const insertResourceSchema = createSelectSchema(resources)
.extend({})
.omit({
id: true,
createdAt: true,
updatedAt: true,
});
export type NewResourceParams = z.infer<typeof insertResourceSchema>;
Create the embeddings schema in lib/db/schema/embedding.ts:
import { nanoid } from '@/lib/utils';
import { index, pgTable, text, varchar, vector } from 'drizzle-orm/pg-core';
import { resources } from './resources';
export const embeddings = pgTable(
'embeddings',
{
id: varchar('id', { length: 191 })
.primaryKey()
.$defaultFn(() => nanoid()),
resourceId: varchar('resource_id', { length: 191 }).references(
() => resources.id,
{ onDelete: 'cascade' },
),
content: text('content').notNull(),
embedding: vector('embedding', { dimensions: 1536 }).notNull(),
},
table => ({
// Create HNSW index for fast vector similarity search
embeddingIndex: index('embeddingIndex').using(
'hnsw',
table.embedding.op('vector_cosine_ops'),
),
}),
);
4. Database Connection Setup
Create lib/db/index.ts:
import { drizzle } from "drizzle-orm/postgres-js";
import postgres from "postgres";
import { env } from "@/lib/env.mjs";
// Create connection
const connectionString = env.DATABASE_URL;
const client = postgres(connectionString, { max: 1 });
export const db = drizzle(client);
5. Migration Setup
Create lib/db/migrate.ts:
import { migrate } from "drizzle-orm/postgres-js/migrator";
import { db } from "./index";
async function main() {
console.log("Running migrations...");
await migrate(db, { migrationsFolder: "./lib/db/migrations" });
console.log("Migrations completed!");
process.exit(0);
}
main().catch((err) => {
console.error("Migration failed:", err);
process.exit(1);
});
6. Generate and Run Migrations
# Generate migrations
npm run db:generate
# Run migrations
npm run db:migrate
Embedding System Implementation
The embedding system is the heart of our RAG implementation. It converts text into vector representations that can be efficiently searched.
1. Core Embedding Functions
Create lib/ai/embedding.ts:
import { embed, embedMany } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { db } from '../db';
import { sql, desc, gt } from 'drizzle-orm';
import { embeddings } from '../db/schema/embedding';
import { getMaximLogger } from '../maxim';
// Use OpenAI's efficient embedding model
const embeddingModel = openai.embedding('text-embedding-3-small');
/**
* Generate text chunks for embedding
* For now, we store content as single chunks to preserve completeness
*/
const generateChunks = (input: string): string[] => {
return [input.trim()].filter(i => i !== '');
};
/**
* Generate embeddings for multiple text chunks
*/
export const generateEmbeddings = async (
value: string,
): Promise<Array<{ embedding: number[]; content: string }>> => {
const chunks = generateChunks(value);
const { embeddings } = await embedMany({
model: embeddingModel,
values: chunks,
});
return embeddings.map((e, i) => ({ content: chunks[i], embedding: e }));
};
/**
* Generate a single embedding for search queries
*/
export const generateEmbedding = async (value: string): Promise<number[]> => {
const input = value.replaceAll('\n', ' ');
const { embedding } = await embed({
model: embeddingModel,
value: input,
});
return embedding;
};
2. Vector Similarity Search
Add the search function to lib/ai/embedding.ts:
/**
* Find relevant content using vector similarity search
* This is the core RAG retrieval function
*/
export const findRelevantContent = async (userQuery: string, sessionId?: string) => {
const maximLogger = await getMaximLogger();
const startTime = Date.now();
try {
// Log search initiation for observability
if (maximLogger) {
console.log('Maxim: Starting vector search', {
operation: 'findRelevantContent',
queryLength: userQuery.length,
queryWords: userQuery.split(' ').length,
model: 'text-embedding-3-small',
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
});
}
// Generate embedding for the user query
const userQueryEmbedded = await generateEmbedding(userQuery);
// Perform vector similarity search using pgvector
const query = sql`
select content, 1 - (embedding <=> ${JSON.stringify(userQueryEmbedded)}::vector) as similarity
from embeddings
where 1 - (embedding <=> ${JSON.stringify(userQueryEmbedded)}::vector) > 0.3
order by similarity desc
limit 4
`;
const result = await (db as any).execute(query);
const rows = (result as any).rows || result;
const searchResults = (rows as Array<{ content: string; similarity: number }>).map(r => ({
name: r.content,
similarity: r.similarity
}));
const duration = Date.now() - startTime;
const maxSimilarity = searchResults.length > 0 ? Math.max(...searchResults.map(r => r.similarity)) : 0;
// Log successful search results
if (maximLogger) {
console.log('Maxim: Vector search completed', {
operation: 'findRelevantContent',
status: 'success',
resultCount: searchResults.length,
maxSimilarity: maxSimilarity.toFixed(3),
duration,
threshold: 0.3,
limit: 4,
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
});
}
return searchResults;
} catch (error) {
const duration = Date.now() - startTime;
// Log errors for debugging
if (maximLogger) {
console.log('Maxim: Vector search failed', {
operation: 'findRelevantContent',
status: 'error',
error: error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error',
duration,
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
});
}
throw error;
}
};
Key Concepts Explained:
- Vector Embeddings: Text is converted to 1536-dimensional vectors that capture semantic meaning
- Cosine Similarity: We use the
<=>operator (cosine distance) to find similar content - Similarity Threshold: Only results with >0.3 similarity are returned to ensure relevance
- HNSW Index: Hierarchical Navigable Small World index provides fast approximate nearest neighbor search
RAG Implementation
1. Resource Creation with Embeddings
Create lib/actions/resources.ts:
'use server';
import {
NewResourceParams,
insertResourceSchema,
resources,
} from '@/lib/db/schema/resources';
import { db } from '../db';
import { generateEmbeddings } from '../ai/embedding';
import { embeddings as embeddingsTable } from '../db/schema/embedding';
import { getMaximLogger } from '../maxim';
/**
* Create a new resource and generate its embeddings
* This is called when the AI decides to save new information
*/
export const createResource = async (input: NewResourceParams, sessionId?: string) => {
const maximLogger = await getMaximLogger();
try {
const { content } = insertResourceSchema.parse(input);
const contentLength = content.length;
const wordCount = content.split(' ').length;
// Log resource creation for observability
if (maximLogger) {
console.log('Maxim: Starting resource creation', {
operation: 'createResource',
contentLength,
wordCount,
hasUrl: content.includes('http'),
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
});
}
// Insert the resource into the database
const [resource] = await db
.insert(resources)
.values({ content })
.returning();
// Generate embeddings for the content
const embeddings = await generateEmbeddings(content);
// Store embeddings in the vector database
await db.insert(embeddingsTable).values(
embeddings.map(embedding => ({
resourceId: resource.id,
...embedding,
})),
);
// Log successful completion
if (maximLogger) {
console.log('Maxim: Resource creation completed', {
operation: 'createResource',
status: 'success',
resourceId: resource.id,
embeddingCount: embeddings.length,
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
});
}
return 'Resource successfully created and embedded.';
} catch (error) {
// Log and handle errors
if (maximLogger) {
console.log('Maxim: Resource creation failed', {
operation: 'createResource',
status: 'error',
error: error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error',
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
});
}
return error instanceof Error && error.message.length > 0
? error.message
: 'Error, please try again.';
}
};
2. Resource Retrieval API
Create app/api/resources/route.ts:
import { NextResponse } from 'next/server';
import { db } from '@/lib/db';
import { resources } from '@/lib/db/schema/resources';
/**
* GET endpoint to retrieve all stored resources
* Used by the frontend to display the knowledge base
*/
export async function GET() {
try {
const allResources = await db.select().from(resources);
return NextResponse.json(allResources);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching resources:', error);
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: 'Failed to fetch resources' },
{ status: 500 }
);
}
}
RAG Workflow Explained:
- Input Processing: User provides text content
- Content Storage: Text is stored in the resources table
- Embedding Generation: Content is converted to vector embeddings
- Vector Storage: Embeddings are stored with HNSW index for fast retrieval
- Similarity Search: When queried, similar content is found using cosine similarity
- Context Retrieval: Relevant content is returned to provide context for AI responses
Maxim AI Integration for Observability
Observability is crucial for understanding and improving your AI system's performance. Maxim AI provides comprehensive monitoring and logging capabilities.
1. Maxim Configuration
Create lib/maxim.ts:
import { Maxim } from '@maximai/maxim-js';
import { env } from './env.mjs';
// Global singleton Maxim logger instance
let maximInstance: Maxim | null = null;
let maximLogger: any = null;
let maximInitialized = false;
/**
* Get or create a Maxim logger instance
* Uses singleton pattern to avoid multiple initializations
*/
export async function getMaximLogger() {
if (maximInitialized && maximLogger) {
return maximLogger;
}
try {
if (env.MAXIM_API_KEY && env.MAXIM_LOG_REPO_ID) {
// Create Maxim instance if it doesn't exist
if (!maximInstance) {
maximInstance = new Maxim({ apiKey: env.MAXIM_API_KEY });
}
// Initialize logger with repository ID
const logger = await maximInstance.logger({ id: env.MAXIM_LOG_REPO_ID });
maximLogger = logger;
maximInitialized = true;
console.log('Maxim logger initialized successfully');
return logger;
}
} catch (error) {
console.warn('Failed to initialize Maxim logger:', error);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Get the Maxim instance for additional functionality
*/
export function getMaximInstance() {
if (!maximInstance && env.MAXIM_API_KEY) {
maximInstance = new Maxim({ apiKey: env.MAXIM_API_KEY });
}
return maximInstance;
}
2. Observability Features
Maxim AI provides several key observability features:
Session Tracking:
- Track entire conversation sessions with unique IDs
- Monitor user engagement, session duration, metrics (latency, inference cost & no. of tokens), LLM & tool calls.
- Analyze conversation patterns and topics
Error Tracking:
- Automatic error capture and categorization
- Stack trace analysis and debugging information
- Alert (Slack or Pagerduty) configuration for critical failures
3. Logging Best Practices
Throughout our application, we implement structured logging:
// Example logging pattern used throughout the codebase
if (maximLogger) {
console.log('Maxim: Operation name', {
operation: 'operationName',
status: 'success' | 'error' | 'in_progress',
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
duration: Date.now() - startTime,
// Additional context-specific fields
});
}
AI Chat API with Tools
1. Core Chat API Implementation
Create app/api/chat/route.ts:
import { createResource } from '@/lib/actions/resources';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import {
convertToModelMessages,
generateText,
tool,
UIMessage,
stepCountIs,
} from 'ai';
import { z } from 'zod';
import { findRelevantContent } from '@/lib/ai/embedding';
import { wrapMaximAISDKModel, MaximVercelProviderMetadata } from '@maximai/maxim-js/vercel-ai-sdk';
import { getMaximLogger } from '@/lib/maxim';
import { env } from '@/lib/env.mjs';
// Allow streaming responses up to 30 seconds
export const maxDuration = 30;
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages, sessionId: bodySessionId }: { messages: UIMessage[]; sessionId?: string } = await req.json();
// Handle session ID from body or cookies
const cookieHeader = req.headers.get('cookie') || '';
const cookieSessionId = cookieHeader
.split(';')
.map((c) => c.trim())
.find((c) => c.startsWith('sessionId='))
?.split('=')[1];
const sessionId = bodySessionId || cookieSessionId || 'unknown';
// Initialize Maxim logger and wrap the AI model
const logger = await getMaximLogger();
if (!logger) {
throw new Error("Maxim logger is not available");
}
const model = wrapMaximAISDKModel(openai('gpt-4o'), logger);
// Extract conversation context for logging
const lastUserMessage = messages.filter(m => m.role === 'user').pop();
const messageCount = messages.length;
const hasTools = messages.some(m => m.parts?.some(p => p.type?.includes('tool')));
const lastUserContent = lastUserMessage?.parts?.find(p => p.type === 'text')?.text || 'unknown';
2. Advanced System Prompt
The system prompt is crucial for RAG behavior:
const result = await generateText({
model,
messages: convertToModelMessages(messages),
stopWhen: stepCountIs(5), // Prevent infinite tool loops
toolChoice: 'auto',
system: `You are a helpful RAG assistant.
- First, answer directly using your general world knowledge when the question is generic and does not require workspace-specific context.
- When the question likely depends on the user's knowledge base (e.g., refers to prior resources, company/app-specific data, or you are uncertain), call the getInformation tool to retrieve relevant context and ground your answer.
- When the user provides new factual information to remember (or explicitly asks you to save it), call the addResource tool. Store a concise version (no metadata chatter), preserving exact facts.
- Prefer one clear final answer. If using tool results, cite or integrate them naturally.
- If after reasonable effort you still lack sufficient information, respond with "Sorry, I don't know." and suggest what info is needed.`,
3. Maxim Observability Configuration
providerOptions: {
maxim: {
sessionName: `RAG-Chat-${sessionId || 'unknown'}`,
sessionId: sessionId,
traceName: `Chat Session - ${messageCount} messages`,
spanName: 'RAG Assistant Response',
generationName: 'GPT-4o RAG Response',
sessionTags: {
application: 'maxim-vercel-rag',
version: '1.0.0',
environment: env.NODE_ENV,
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
},
traceTags: {
endpoint: '/api/chat',
type: 'conversation',
messageCount: messageCount.toString(),
hasTools: hasTools.toString(),
userQuery: lastUserContent.substring(0, 100),
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
},
spanTags: {
model: 'gpt-4o',
provider: 'openai',
streaming: 'false',
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
},
generationTags: {
temperature: '0.7',
maxTokens: '4000',
tools: 'addResource,getInformation',
sessionId: sessionId || 'unknown',
},
} as MaximVercelProviderMetadata,
},
4. Tool Definitions
tools: {
addResource: tool({
description: `add a resource to your knowledge base.
If the user provides a random piece of knowledge unprompted, use this tool without asking for confirmation.`,
inputSchema: z.object({
content: z
.string()
.describe('the content or resource to add to the knowledge base'),
}),
execute: async ({ content }) => createResource({ content }, sessionId),
}),
getInformation: tool({
description: `get information from your knowledge base to answer questions.`,
inputSchema: z.object({
question: z.string().describe('the users question'),
}),
execute: async ({ question }) => findRelevantContent(question, sessionId),
}),
},
});
return Response.json({ text: result.text });
Tool Decision Logic:
- addResource Tool: Automatically triggered when users share new information
- getInformation Tool: Called when the AI needs context from the knowledge base
- Intelligent Routing: The AI decides which tool to use based on conversation context
Frontend Implementation
1. Custom Chat Hook
Create lib/hooks/useChatWithSession.ts:
import { useChat } from '@ai-sdk/react';
import { useState, useCallback } from 'react';
export function useChatWithSession(sessionId: string) {
const [messages, setMessages] = useState<any[]>([]);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const sendMessage = useCallback(async (message: { text: string }) => {
if (isLoading) return;
setIsLoading(true);
// Add user message to local state
const userMessage = {
id: Date.now().toString(),
role: 'user',
parts: [{ type: 'text', text: message.text }]
};
setMessages(prev => [...prev, userMessage]);
try {
// Send message to chat API
const response = await fetch('/api/chat', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Accept': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
messages: [...messages, userMessage],
sessionId: sessionId,
}),
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error('Failed to send message');
}
const data = await response.json();
const assistantText = data.text ?? '';
// Add assistant response to messages
const assistantMessage = {
id: (Date.now() + 1).toString(),
role: 'assistant',
parts: [{ type: 'text', text: assistantText }],
};
setMessages(prev => [...prev, assistantMessage]);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error sending message:', error);
} finally {
setIsLoading(false);
}
}, [messages, sessionId, isLoading]);
return { messages, sendMessage, isLoading };
}
2. Main Chat Interface
Create a comprehensive chat interface in app/page.tsx:
'use client';
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { Bot, User, Database, Search, Sparkles, ArrowRight, BookOpen, Zap } from 'lucide-react';
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from 'uuid';
import { useChatWithSession } from '@/lib/hooks/useChatWithSession';
interface Resource {
id: string;
content: string;
createdAt: string;
}
export default function Chat() {
const [input, setInput] = useState('');
const [resources, setResources] = useState<Resource[]>([]);
const [flashingTool, setFlashingTool] = useState<string | null>(null);
const [sessionId, setSessionId] = useState<string>('');
const { messages, sendMessage, isLoading } = useChatWithSession(sessionId);
// Fetch resources from the API
const fetchResources = async () => {
try {
const response = await fetch('/api/resources');
if (response.ok) {
const data = await response.json();
setResources(data);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to fetch resources:', error);
}
};
// Generate unique session ID on mount
useEffect(() => {
const newSessionId = uuidv4();
setSessionId(newSessionId);
try {
document.cookie = `sessionId=${newSessionId}; path=/; sameSite=Lax`;
} catch {}
console.log('New session started:', newSessionId);
}, []);
// Load resources on component mount
useEffect(() => {
fetchResources();
}, []);
// Handle tool execution visual feedback
useEffect(() => {
messages.forEach(message => {
message.parts.forEach((part: any) => {
if (part.type === 'tool-addResource' || part.type === 'tool-getInformation') {
if (part.state === 'output-available') {
setFlashingTool(part.type);
setTimeout(() => setFlashingTool(null), 2000);
// Refresh resources when a new one is added
if (part.type === 'tool-addResource') {
setTimeout(fetchResources, 500);
}
}
}
});
});
}, [messages]);
3. UI Components and Styling
The interface includes several key sections:
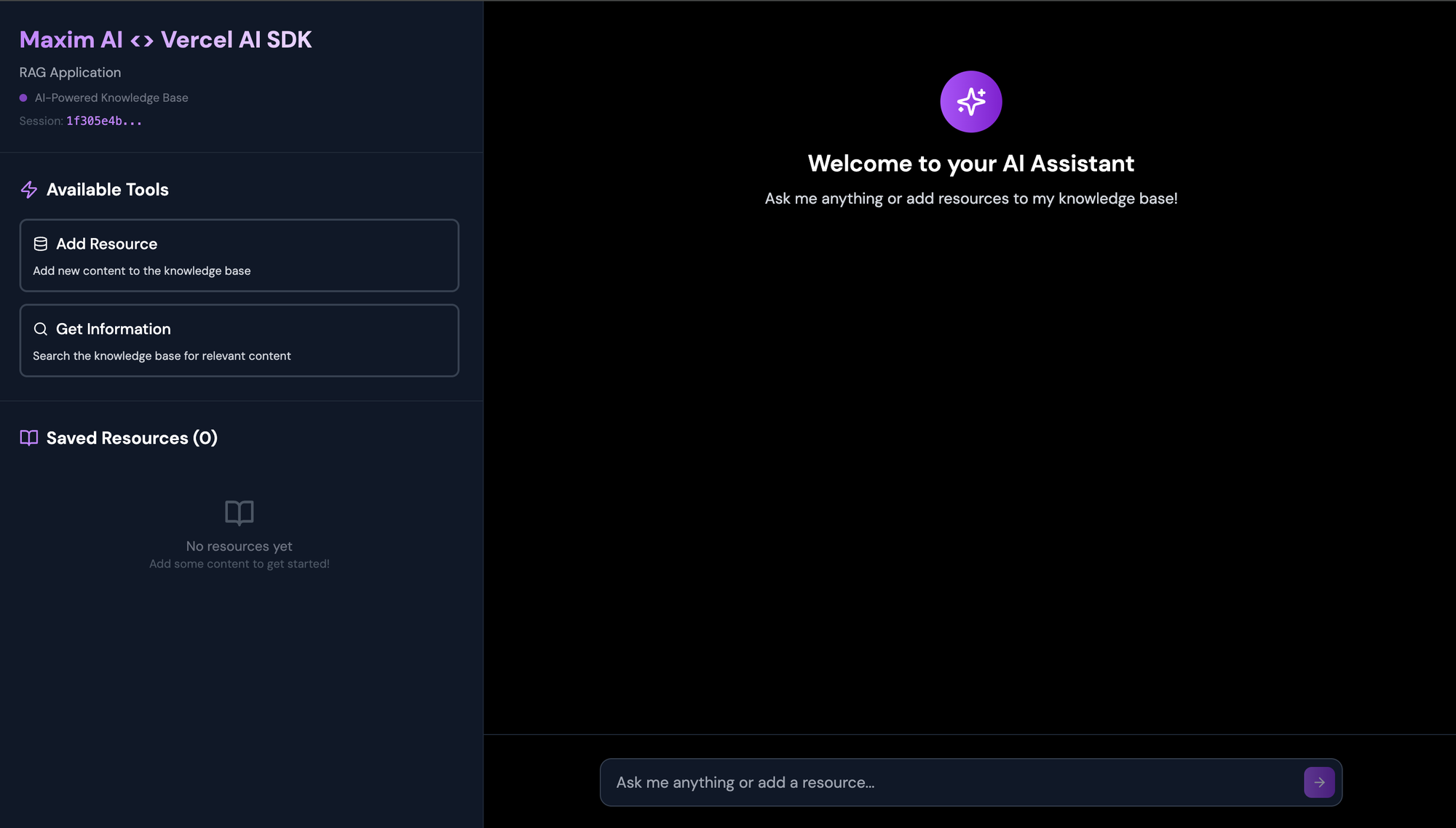
Sidebar with Knowledge Base:
{/* Sidebar */}
<div className="w-1/3 bg-gray-900 border-r border-gray-800 flex flex-col">
{/* Header */}
<div className="p-6 border-b border-gray-800">
<h1 className="text-2xl font-bold bg-gradient-to-r from-purple-400 to-white bg-clip-text text-transparent mb-2">
Maxim AI <> Vercel AI SDK
</h1>
<p className="text-sm text-gray-400">RAG Application</p>
<div className="flex items-center gap-2 mt-2">
<div className="w-2 h-2 bg-purple-500 rounded-full animate-pulse"></div>
<span className="text-xs text-gray-500">AI-Powered Knowledge Base</span>
</div>
{sessionId && (
<div className="mt-2 text-xs text-gray-600">
Session: <span className="font-mono text-purple-400">{sessionId.substring(0, 8)}...</span>
</div>
)}
</div>
{/* Tools Section */}
<div className="p-6 border-b border-gray-800">
<h2 className="text-lg font-semibold text-white mb-4 flex items-center gap-2">
<Zap className="w-5 h-5 text-purple-400" />
Available Tools
</h2>
<div className="space-y-3">
<div className={`p-3 rounded-lg border-2 ${getToolColor('tool-addResource')}`}>
<div className="flex items-center gap-2 mb-2">
<Database className="w-4 h-4" />
<span className="font-medium">Add Resource</span>
</div>
<p className="text-xs text-gray-300">Add new content to the knowledge base</p>
</div>
<div className={`p-3 rounded-lg border-2 ${getToolColor('tool-getInformation')}`}>
<div className="flex items-center gap-2 mb-2">
<Search className="w-4 h-4" />
<span className="font-medium">Get Information</span>
</div>
<p className="text-xs text-gray-300">Search the knowledge base for relevant content</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* Resources Section */}
<div className="flex-1 p-6 overflow-y-auto">
<h2 className="text-lg font-semibold text-white mb-4 flex items-center gap-2">
<BookOpen className="w-5 h-5 text-purple-400" />
Saved Resources ({resources.length})
</h2>
<div className="space-y-3">
{resources.length === 0 ? (
<div className="text-center py-8">
<BookOpen className="w-8 h-8 text-gray-600 mx-auto mb-2" />
<p className="text-sm text-gray-500">No resources yet</p>
<p className="text-xs text-gray-600">Add some content to get started!</p>
</div>
) : (
resources.map((resource) => (
<div key={resource.id} className="bg-gray-800 rounded-lg p-3 border border-gray-700">
<p className="text-sm text-white line-clamp-3 mb-2">{resource.content}</p>
<p className="text-xs text-gray-400">
{new Date(resource.createdAt).toLocaleDateString()}
</p>
</div>
))
)}
</div>
</div>
</div>
Chat Interface:
{/* Main Chat Area */}
<div className="flex-1 flex flex-col">
{/* Chat Container */}
<div className="flex-1 overflow-y-auto p-6">
<div className="max-w-3xl mx-auto space-y-6">
{messages.length === 0 && (
<div className="text-center py-12">
<div className="w-16 h-16 bg-gradient-to-r from-purple-500 to-purple-700 rounded-full flex items-center justify-center mx-auto mb-4">
<Sparkles className="w-8 h-8 text-white" />
</div>
<h2 className="text-2xl font-semibold text-white mb-2">Welcome to your AI Assistant</h2>
<p className="text-gray-300">Ask me anything or add resources to my knowledge base!</p>
</div>
)}
{messages.map(m => (
<div key={m.id} className="flex gap-4">
{/* Avatar */}
<div className={`w-8 h-8 rounded-full flex items-center justify-center flex-shrink-0 ${
m.role === 'user'
? 'bg-white text-black'
: 'bg-gradient-to-r from-purple-500 to-purple-700 text-white'
}`}>
{m.role === 'user' ? <User className="w-4 h-4" /> : <Bot className="w-4 h-4" />}
</div>
{/* Message Content */}
<div className="flex-1 space-y-3">
<div className="font-semibold text-gray-300 capitalize">{m.role}</div>
{m.parts.map((part: any, index: number) => {
switch (part.type) {
case 'text':
return (
<div key={index} className="prose prose-sm max-w-none">
<p className="text-white leading-relaxed">{part.text}</p>
</div>
);
case 'tool-addResource':
case 'tool-getInformation':
return (
<div key={index} className={`rounded-lg border-2 p-4 ${getToolColor(part.type)}`}>
<div className="flex items-center gap-2 mb-3">
{getToolIcon(part.type)}
<span className="font-semibold">
{part.state === 'output-available' ? 'Tool Executed' : 'Executing Tool'}
</span>
<span className="text-xs bg-gray-800 px-2 py-1 rounded-full">
{part.type.replace('tool-', '')}
</span>
</div>
<div className="bg-gray-800 rounded-md p-3">
<div className="text-sm font-medium mb-2 text-gray-300">Input:</div>
<pre className="text-xs overflow-x-auto text-gray-200">
{JSON.stringify(part.input, null, 2)}
</pre>
</div>
{part.state === 'output-available' && part.output ? (
<div className="mt-3 bg-gray-800 rounded-md p-3">
<div className="text-sm font-medium mb-2 text-gray-300">Output:</div>
<div className="text-xs text-gray-200">
{typeof part.output === 'string'
? part.output
: JSON.stringify(part.output as any, null, 2)
}
</div>
</div>
) : null}
</div>
);
default:
return null;
}
})}
</div>
</div>
))}
4. Interactive Features
Visual Tool Feedback:
const getToolColor = (toolType: string) => {
const isFlashing = flashingTool === toolType;
const baseClasses = 'bg-gray-900 border-gray-700 text-white';
const flashClasses = 'bg-green-900 border-green-500 text-white animate-pulse';
if (isFlashing) return flashClasses;
switch (toolType) {
case 'tool-addResource':
return baseClasses;
case 'tool-getInformation':
return baseClasses;
default:
return 'bg-gray-900 border-purple-500 text-white';
}
};
Form Handling:
<form
onSubmit={e => {
e.preventDefault();
if (input.trim()) {
sendMessage({ text: input });
setInput('');
}
}}
className="flex gap-3"
>
<div className="flex-1 relative">
<input
className="w-full px-4 py-3 pr-12 bg-gray-900 border border-gray-700 text-white rounded-xl focus:outline-none focus:ring-2 focus:ring-purple-500 focus:border-transparent shadow-sm placeholder-gray-400"
value={input}
placeholder="Ask me anything or add a resource..."
onChange={e => setInput(e.currentTarget.value)}
/>
<button
type="submit"
disabled={!input.trim()}
className="absolute right-2 top-1/2 transform -translate-y-1/2 p-2 bg-gradient-to-r from-purple-500 to-purple-700 text-white rounded-lg hover:from-purple-600 hover:to-purple-800 disabled:opacity-50 disabled:cursor-not-allowed transition-all"
>
<ArrowRight className="w-4 h-4" />
</button>
</div>
</form>
Testing & Deployment
1. Local Development
# Start the development server
npm run dev
# Run database migrations
npm run db:migrate
# View database in Drizzle Studio
npm run db:studio
2. Testing the System
Test RAG Functionality:
- Start a conversation: "Hello, I'm building a React app"
- Add knowledge: "I'm using Next.js 14 with TypeScript and Tailwind CSS"
- Query knowledge: "What technologies am I using for my app?"
- Verify tool execution and knowledge retrieval
Test Observability:
- Check Maxim AI dashboard for session tracking
- Monitor tool execution logs
- Verify error handling and logging
3. Production Deployment
Environment Setup:
# Set production environment variables
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_production_openai_key
DATABASE_URL=your_production_database_url
MAXIM_API_KEY=your_production_maxim_key
MAXIM_LOG_REPO_ID=your_production_repo_id
NODE_ENV=production
Vercel Deployment:
# Deploy to Vercel
npx vercel --prod
# Set environment variables in Vercel dashboard
# Configure database with pgvector support
Advanced Features
1. Enhanced Chunking Strategy
For larger documents, implement intelligent chunking:
const generateChunks = (input: string): string[] => {
const maxChunkSize = 1000;
const overlap = 200;
if (input.length <= maxChunkSize) {
return [input.trim()];
}
const chunks = [];
let start = 0;
while (start < input.length) {
const end = Math.min(start + maxChunkSize, input.length);
let chunk = input.slice(start, end);
// Find the last sentence boundary
if (end < input.length) {
const lastSentence = chunk.lastIndexOf('.');
if (lastSentence > chunk.length * 0.5) {
chunk = chunk.slice(0, lastSentence + 1);
}
}
chunks.push(chunk.trim());
start += chunk.length - overlap;
}
return chunks.filter(chunk => chunk.length > 0);
};
2. Semantic Search Improvements
Implement hybrid search combining vector similarity and keyword matching:
export const hybridSearch = async (query: string, sessionId?: string) => {
// Vector similarity search
const vectorResults = await findRelevantContent(query, sessionId);
// Keyword search using PostgreSQL full-text search
const keywordQuery = sql`
SELECT content, ts_rank(to_tsvector('english', content), plainto_tsquery('english', ${query})) as rank
FROM embeddings
WHERE to_tsvector('english', content) @@ plainto_tsquery('english', ${query})
ORDER BY rank DESC
LIMIT 4
`;
const keywordResults = await (db as any).execute(keywordQuery);
// Combine and deduplicate results
const combinedResults = [...vectorResults, ...keywordResults]
.filter((result, index, self) =>
index === self.findIndex(r => r.content === result.content)
)
.sort((a, b) => (b.similarity || b.rank) - (a.similarity || a.rank))
.slice(0, 6);
return combinedResults;
};
3. Conversation Memory
Implement conversation context retention:
// Add to chat API
const conversationContext = messages
.filter(m => m.role === 'user' || m.role === 'assistant')
.slice(-6) // Keep last 6 messages for context
.map(m => `${m.role}: ${m.content}`)
.join('\n');
// Include in system prompt
const systemPrompt = `${baseSystemPrompt}
Recent conversation context:
${conversationContext}
Use this context to provide more relevant responses.`;
4. Advanced Analytics
Implement detailed analytics tracking:
// Add to Maxim logging
const analytics = {
userEngagement: {
sessionDuration: Date.now() - sessionStartTime,
messageCount: messages.length,
toolUsageCount: messages.filter(m => m.parts?.some(p => p.type?.includes('tool'))).length,
},
knowledgeBase: {
totalResources: await db.select({ count: sql`count(*)` }).from(resources),
searchQueries: searchCount,
resourceAdditions: addResourceCount,
},
performance: {
averageResponseTime: totalResponseTime / responseCount,
vectorSearchLatency: averageSearchTime,
embeddingGenerationTime: averageEmbeddingTime,
}
};
if (maximLogger) {
console.log('Maxim: Session analytics', analytics);
}
5. Multi-Modal Support
Extend the system to handle different content types:
// Enhanced resource schema
export const resources = pgTable("resources", {
id: varchar("id", { length: 191 }).primaryKey().$defaultFn(() => nanoid()),
content: text("content").notNull(),
contentType: varchar("content_type", { length: 50 }).notNull().default('text'),
metadata: json("metadata"), // Store additional metadata
source: varchar("source", { length: 255 }), // Track content source
tags: text("tags").array(), // Add tagging support
createdAt: timestamp("created_at").notNull().default(sql`now()`),
updatedAt: timestamp("updated_at").notNull().default(sql`now()`),
});
// Support for different content types
const processContent = async (content: string, contentType: string) => {
switch (contentType) {
case 'url':
// Fetch and extract content from URL
const webContent = await extractWebContent(content);
return generateEmbeddings(webContent);
case 'file':
// Process uploaded files
const fileContent = await processFile(content);
return generateEmbeddings(fileContent);
case 'text':
default:
return generateEmbeddings(content);
}
};
Conclusion
You've successfully built a comprehensive Second Brain AI Agent with:
✅ RAG Implementation: Vector-based knowledge storage and retrieval
✅ AI Tools Integration: Intelligent tool selection and execution
✅ Observability: Complete monitoring with Maxim AI
✅ Modern UI: Beautiful, responsive chat interface
✅ Production Ready: Scalable architecture with proper error handling
Next Steps
- Scale the Knowledge Base: Add support for documents, PDFs, and web scraping
- Improve Search: Implement hybrid search combining vector and keyword approaches
- Add Authentication: Implement user management and personalized knowledge bases
Resources
Happy building! 🚀